Table Of Content
If you have darker skin, your doctor may prescribe skin bleachingcream. It's important that your skin is as light as possible for the procedure. If you're not happy with shaving, tweezing, or waxing to remove unwanted hair, laser hair removal may be an option worth considering. Only the skin surface is affected by the lasers, so the minimal radiation from the procedure can’t penetrate to any of your organs. In fact, according to the Skin Care Foundation, the procedure is sometimes used to treat certain forms of precancerous lesions. In some cases, laser hair removal may lead to excessive hair growth in the treated area.
Does IPL Laser Hair Removal Cause Cancer
Can Lasering Your Bikini Area Cause Infertility? - Allure
Can Lasering Your Bikini Area Cause Infertility?.
Posted: Wed, 30 Jan 2013 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Boasting a stellar reputation, Dr. Agarwal is not only acclaimed by her team but also by a multitude of satisfied former and current patients. Her commitment to ethical practices ensures that every skincare solution she provides is not only effective but also aligned with the highest standards of professionalism. Here, we explore the safety measures and regulations in place to maintain the integrity of laser hair removal as a cosmetic procedure.
Risks
They can provide you with guidance on how to manage the side effects and minimize the risk of complications. While laser hair removal is generally considered safe, there are potential side effects that patients should be aware of. Most people experience hair removal that lasts several months, and it might last for years. Home-use treatments such as fractional laser treatments may ulcerate melanoma causing the patient to seek further advice and provide appropriate treatment.
How is the Procedure Performed?
For instance, people with a genetic predisposition to skin cancer, such as those with a family history of the disease or certain genetic mutations, may have an elevated risk. These genetic factors can affect how the skin responds to UV radiation, making it more susceptible to developing skin cancer. Studies have been conducted to evaluate the potential risks of laser hair removal, including the possibility of DNA damage. One study published in the Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery investigated the effects of laser hair removal on DNA in the skin cells. The study found that while laser hair removal did cause some damage to the DNA in skin cells, the damage was minimal and easily repaired by the body's natural repair mechanisms. Laser hair removal has become a popular method for removing unwanted hair from various parts of the body.
However, with a limited sampling and uncertainty, whether the laser treatment was a contributor in the development is unknown. No, there is no evidence to suggest that getting laser hair removal causes skin cancer. Laser hair removal works by targeting the melanin in hair follicles, destroying them without causing harm to the surrounding skin cells. The laser used in this procedure emits a specific wavelength of light that is absorbed by the pigment in the hair follicles, resulting in their destruction.
New Study Says Laser Hair Removal Dangerous, Chemicals Released - STYLECASTER
New Study Says Laser Hair Removal Dangerous, Chemicals Released.
Posted: Thu, 11 Jul 2013 07:00:00 GMT [source]
These devices are designed for consumer use and have been subject to regulatory oversight by relevant health authorities in different countries. Laser hair removal isn't recommended for eyelids, eyebrows or surrounding areas, due to the possibility of severe eye injury. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Talk to your doctor about which medications to stop if you're on any anti-inflammatories or regularly take aspirin.
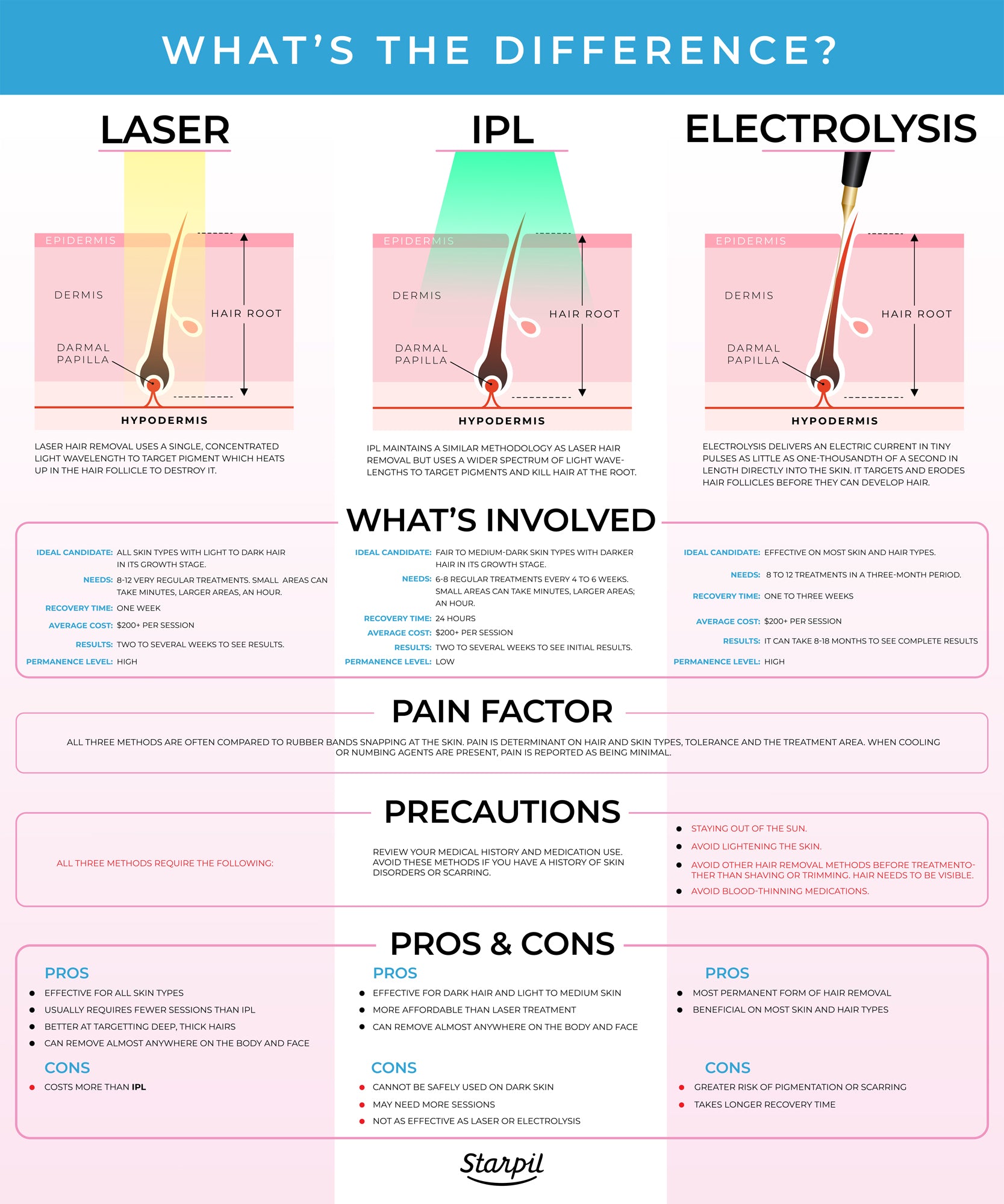
What her facialist wanted to remove with a laser was actually a deep squamous cell carcinoma, a type of skin cancer. It’s the heat from the laser that damages the follicle, inhibiting hair growth, but this localized effect is not known to induce any sort of cellular changes that could lead to cancer. Laser hair removal utilizes non-ionizing radiation, which is a type of radiation that doesn’t carry enough energy to ionize (remove an electron) from an atom or molecule. The amount of time hair removal lasts until the next session varies, but the average hair clearance rate with current hair removal technology is 20%-75% after one to six months of follow-up treatments. The length of treatment depends on the size of the area being treated. For example, treating a large area like the back may take more than an hour, but a smaller area like the upper lip may only take a few minutes.
The Importance of Laser Hair Removal Safety
Only an experienced healthcare provider should perform the procedure. There is limited research on the safety of laser hair removal during pregnancy, so it is generally not recommended. If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, it is important to discuss any concerns you may have with your healthcare provider. If you experience side effects, such as redness or blistering, after undergoing laser hair removal, it is important to consult with your provider.
For people looking to stick with more traditional hair removal methods, Bowe recommends shaving. Go back to the practitioner who treated you if you have any complications that need medical attention. If this is not possible, see a GP or go to your nearest accident and emergency (A&E). They then press a handheld device to your skin and trigger the laser.
They should treat the affected skin as if it had been sunburned to avoid further damage. This means keeping it moisturized, protected from light, and checked regularly for signs of infection. This means there is a risk of potentially serious eye injury, especially when a practitioner is working on a person’s face. By taking care of the treated area after laser removal, such as by using a moisturizer, a person may prevent any lasting issues from this treatment. Anyone experiencing lasting side effects should consult their dermatologist.
One such concern is whether the laser used in hair removal treatments can damage the DNA in skin cells, potentially leading to skin cancer. It is worth noting that, like any other medical procedure, laser hair removal does carry some risks. These risks include skin irritation, redness, and temporary changes in skin pigmentation.
Laser hair removal has also been observed to affect the appearance of moles. While this does not cause skin cancer, it could potentially cause a benign mole to appear cancerous, or, worse, cause a melanoma to appear benign. If you’re concerned about skin cancer, it may be a good idea to have any suspicious moles checked before beginning laser hair removal treatment. As of now, no research has showed the light energy from hair removal lasers can cause cancer. But there are some risks involved like redness, scarring and discoloration in the treated area, Bowe said.
While minor side effects may occur, the risk of serious complications, including cancer, is extremely low. Individuals considering laser hair removal should consult with a qualified practitioner to discuss their concerns and ensure personalized treatment tailored to their specific needs. There is a common misconception that the heat generated during laser hair removal could lead to cancerous changes in the skin cells. However, it’s important to note that the energy levels used in laser hair removal treatments are carefully controlled and not sufficient to cause mutations or cancer. Extensive research to date has not shown a direct link between laser hair removal and an increased risk of developing cancer.
Exposing the treated area to sunlight too soon after laser hair removal can result in blisters and skin crusting. There is no scientific evidence that concludes or suggests that laser hair removal causes cancer. In the United States, cosmetic lasers are regulated by the FDA, and manufacturers must demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their devices before they can be marketed for hair removal. These devices are then classified and must comply with performance standards. This means that the laser used in the procedure doesn’t damage DNA, and therefore, cannot lead directly to cancers, in contrast to ionizing radiation from X-rays or ultraviolet light which can lead to DNA damage. Most people will need approximately six to eight sessions, spaced six to eight weeks apart, to see long-lasting results.

No comments:
Post a Comment